Xn Tf P
Solutions to Additional Problems 416 Find the FT representations for the following periodic signals Sketch the magnitude and phase spectra (a) x(t) = 2cos(πt) sin(2πt) x(t)=ejπt e−jπt 1.

Xn tf p. 1;;X n be iid random variables where the common distribution is a Bernoulli distribution with parameter p We know that the expected value of the Bernoulli distribution is pand the variance of a Bernoulli distribution is p(1 p), which is nite Therefore, by the weak law of large numbers, X n!P p Since P n i=1 X i has a b(n;p) distribution. 11 G N W atson* A T reatise on the T heory of B essel F u n ctio n s, C am b rid g e, Znd E dition* 1944c 12 C L an czo s, T ables of C hebyshev P olynom ials S (x) and C (x), N ational B ureau of S tandards A pplied M athem atics S eries 9* D ecem b er, 1952 P R O B L E M D E P A R T M E N T. λ xe−λ (a) To show that T = P n i=1 X i is sufficient for λ, we first note that T has a Poisson distribution with parameter nλ, so we have P (X 1 = x 1, X 2 = x 2,,X n = x nT = t) P (X 1 = x 1,X 2 = x 2,,X n = x n,T = t) P(T = t) = P X 1 = x 1,X 2 = x 2,,X n = t− P n−1 i=1 x i P(T.
YingweiWang MethodsOfAppliedMathematics On the other hand, kx0 − y0k ≤ ky0 −y n k kky n k −x0k → d, as k → ∞ So y0 is just what we want to find 2 Lineartransformation Question Find the norm of the operator A ∈ B(X) given by (Af)(t) = tf(t), 0 ≤ t ≤ 1,. 11 hours ago · Eߣ B† B÷ Bò Bó B‚„webmB‡ B S€g ,x£ M›t@M»‹S«„ I©fS¬ ßM»ŒS«„ T®kS¬‚ 0M» S«„ S»kS¬ƒ,x'ì £ I©f E*×±ƒ B@M€ LavfWA Lavfs¤ å"büÿ4¶ÿñQª_bD‰ˆ@Çp T®k F® =× sÅ œ "µœƒund†V_VP8ƒ #ッþP*à °‚ €º‚ 8T°‚ €Tº‚ 8. Lecture 9 November 8, 18 95 3n2 3100n 6 6= ( n)Only Oapplies 3n2 100n 6 6= ( n)Only applies Interesting Aside Donald Knuth popularized the use of BigO notation It was originally inspired by the use of \ell" numbers, written as L(5), which indicates a number that we don’t.
Problem 9 Proposition 9 Let fX ngbe a collection of independent random variables with PfX n= n2g= 1 n2 and PfX n= 1g= 1 1 n2 for all n In this case, P n i=1 X i converges almost surely to 1 as n!1 Proof Observe rst that, by de nition of the X n, P(X n2fn2;. Jul 01, 12 · This paper deals with the fractional Sobolev spaces Ws,p We analyze the relations among some of their possible definitions and their role in the trac. See the answer Find F(s) L{tU(t − 6)} Expert Answer 100% (33 ratings) Previous question Next question.
N = T(x n), then y n!T(x) by the continuity of T, and f(x n) = d(y n;x n) !d(T(x);x) = f(x) by the continuity of d Since f X!R is a continuous function on a compact set, it attains its minimum value at some a2X If T(a) 6=a, then f(T(a)) = d(T(T(a));T(a)). N = (x n;t n) and z = (x;t), we have x n!x, t n!t, and t n f(x n) Taking the limit of this inequality at n!1, we get that t liminf f(x n), and then the lower semicontinuity of fimplies that t f(x) Hence, z2epif, and epifis closed Remark Semicontinuous functions play an important role in variational. In the same way, in textbooks and when writing things out, we use different function names like f (x), g(x), h(x), s(t), etc, to keep track of, and work with, more than one formula in any single contextWith function notation, we can now use more than one function at a time without confusing ourselves or mixing up the formulas, leaving ourselves wondering "Okay, which ' y ' is this one?".
Transformation T M2,2(R) → M2,3(R) given by T(A) = A 1 1 1 1 0 0 for all 2×2 matrices A Find bases for the range and for the nullspace of T BonusProblem5(15pts) Suppose V1 and V2 are real vector spaces, dimV1 = m, dimV2 = n Let B(V1,V2) denote the subspace of F(V1× V2) consisting of bilinear functions (ie, functions of two. EC02 Spring 06 HW7 Solutions March 11, 06 6 The probability that two laptops need LCD repairs is PN1 (2) = 4 2 (8/15)2(7/15)2 = (4) (c) A repair is type (2) with probability p2 = 4/15 A repair is type (3) with probability. T We will prove this by induction Let M t be a random variable that takes the value of the item in memory at time t We need to show that at time t, PM t = b i = 1/t for all 1 ≤ i ≤ t The base case is when t = 1, which is trivially true since M t = b 1 with probability 1 Assume that at time t, PM t = b i = 1/t for all 1 ≤ i ≤ t.
May 08, 21 · ÝùÄ!€ ª ú{ÎõOq J xÇ X N@„{ u´Ã — ÆP K˜ ¡t(ðTì_S M®¹FšKR0l¿É Ò›C§“n ÿ®€@/k¹‚`ÈÆ,=Ò / —4û 1(%©k £ g¤‘ªeòj ¥ ¡ ¯„ %A E£ Z•1Ý í¼sžÝ "Ž?cÿøk µ,Ôþ4Tœ³¯ÞûýÿÿÏðçöïn· ;r¸å= QN?ò b¼NP¦êtËcN;ù Öÿ{ý~¿ûw Ù¹ ë_,Ï ïpÉô‰H b¯tíü ‹rÈÆ9Ò. I,' 1,7 I I~, I " , ', I , " I I ,I I I I I. 6 hours ago · EߣŸB† B÷ Bò Bó B‚„webmB‡ B S€g >éR M›t»M»‹S«„ I©fS¬ ¡M»‹S«„ T®kS¬ ãM»ŒS«„ TÃgS¬‚ (M» S«„ S»kS¬ƒ>é ì X I©f½*×±ƒ B@M€ LavfWA LavfDaˆ Í “ ¼D‰ˆ@Ö˜ T®kQ?® F× sň0%oå ¯¨Æœ "µœƒund†V_VP8ƒ #ツ ü Uà °‚ º‚ ÐU°ˆU· U¸ ® ç× sňXª®‘ ^qœ "µœƒund†ˆA_VORBISƒ á.
Aug 07, 07 · By induction, then, if f(x)= x n, f'(x)= nx n1 for any positive integer n It is easy to see that the derivative of x 0 is 0(x1)= 0 since x 0 = 1 is a constant To find the derivative of xn, write it as 1/x n and use the quotient rule To find the derivative of x r where r is not an integer, use logarithmic differentiation (You could use the. Math 3113 Multivariable Calculus Homework #8 Due Date Solutions A function f(x,y) is said to be homogeneous of degree n if f(tx,ty) = tnf(x,y) for all t. (x−a)nf(n)(a) because of the difficulty of obtaining the derivatives.
For all points twhere the CDF F X is continuous We will see why the exception matters in a little while but for now it is worth noting that convergence in distribution is the weakest form of convergence We write X n X For instance, a sequence of iid N(0;1) RVs converge in distribution to an independent. Find F(s) L{tU(t − 6)} Question Find F(s) L{tU(t − 6)} This problem has been solved!. 'A ,,,, , , ,_, " _,T," , "' t' '," ' ;1 e, , ',' L' , , ,, , " 1 Ii, 11 " , l, I ,;.
D) y n = 0, 0, 1, 0 ∆x n with ∆ denoting circular convolution Solution a) Since ej p 2 n x n =ej 2 p 4 n x n then DFT ej p 2 n x n =X k1 4 = 1 j,0,1j,1 b) In this case y n =Å1ÅÅÅ 2 ej 2 p 4 n x n ÅÅ1ÅÅ 2 ej 2 p 4 n x n and therefore its DFT is. EC02 Spring 06 HW12 Solutions April 27, 06 6 Problem 1132 • is a sequence of independent random variables such that = 0 for n < 0 while for n ≥ 0, each is a Gaussian (0,1) random variable Passing through the filter h= 1 −1 1 ′ yields the output YnFind the PDFs of. Stack Exchange network consists of 176 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers Visit Stack Exchange.
Example 2 f(x) = x n where n = 1, 2, 3 d In this example we answer the question “What is x n ?” Once we know the dx answer we can use it to, for example, find the derivative of f(x) = x4 by replacing n by 4 At this point in our studies, we only know one tool for finding derivatives – the difference quotient. C 4 ‚ ü X Ò $ &¸Â\@'° F œÁ($ P lCí&‹"„ÁŠD(xg „* T ˆ =øA ô@8Ð 0@ B?ø@" ÂŒ ”A ´B DB Â74@ZÿˆËv Ì"Ä 0@ (À œÃ ¬w Sê®),Ž , hRA ÿ` ¬€ Àçþƒ Ð& €®X @œÙ TÜ ˜ Üz×Üú¦‹ŠŒJTÁDT )fD¾ü „Ýø Ï LÄ ÐÁ œƒ >dÀ, „ÂElBü6^Ër©Â n4 B ¦ loÖnDí= BJèj þÒEàæÐüoõ. OBTAINING TAYLOR FORMULAS Most Taylor polynomials have been bound by other than using the formula pn(x)=f(a)(x−a)f0(a) 1 2!.
Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history. C University of Bristol 14 Further Topics in Analysis Solutions 9 1 Let f 0;1 !R be de ned by f(x) = x Prove that f is Riemann integrable and. X(n) is periodic if x(n) = x(n N) for some integer value of N For the sequence in (a), x (n N) = A cos (27 n N ) x(n N) = x(n) if 7 N is an integer multiple of 27 The smallest value of N for which this is true is N = 14 Therefore the sequence in (a) is periodic with period 14.
Problem 4 (868) X 1,,X n iid with probability mass function function p(xλ) = 1 x!. &Ð( J“¡²"A² ÏWqDì4PfŽt•\y"“ÏLòà¶w‹qB?UÐ™Ô¨Ö 7ÿû’d 7Wʃ/FP&ÀI‰ C Í_(̽5H¯ e 1€ (aÓe aiíÒøþ Ð^Ã\3U / hj JŽ. A polynomial of lower degree than f(x) (or possibly 0) Apply the induction hypothesis to f 1 and g, to obtain polynomials q 1.
That is, provide a function T(n) such that the algorithm will take T(n) steps to produce the output for input n In the table below, show how much time each line will take and then multiply each line by the number of times it will be repeated (in case of the while loop). May 09, 21 · P` «˜rão ÷ÉçðXT‹hn%P$ e çk ¢ °R H€X¡Y"!. These are found in the main IPA article or on the extensive IPA chartFor the Manual of Style guideline for pronunciation, see WikipediaManual of Style/Pronunciation.
Solutions to Assignment7 (Due 07/30) Please hand in all the 8 questions in red 1Consider the sequence of functions f n 0;1 !R de ned by f n(x) = x2 x2 (1 nx)2 (a)Show that the sequence of functions converges pointwise as n!1, and compute the limit function. (t) = F X(t);. I=1 i= n(n 1) 2 Geometric series X1 i=0 ai= 1 1 a for 0.
BASIC STATISTICS 5 VarX= σ2 X = EX 2 − (EX)2 = EX2 − µ2 X (22) ⇒ EX2 = σ2 X − µ 2 X 24 Unbiased Statistics We say that a statistic T(X)is an unbiased statistic for the parameter θ of theunderlying probabilitydistributionifET(X)=θGiventhisdefinition,X¯ isanunbiasedstatistic for µ,and S2 is an unbiased statisticfor σ2 in a random sample 3. Sep 28, 09 · Eg x*x^(n2)*y cancels y*x^(n1), x*x^(n3)*y^2 cancels y*x^(n2)*y I know you can't write out all of the terms You'll have to use the '' to express what you mean It might help to write the two expanded products on separate lines and shift one over so cancelling terms are above each other Last edited Sep 27, 09. Using the Invariance Principle, we can use p^which was found in part(a).
®o §µ4cÜhù ‚ éNäfÖ †‹* °xæ ©mºäw*´»jü»ôæÿÿGGÿô Ò¼“ Æô «T@5( éØm— ‰,l¦ r ;ËØaT¥ !. Mar 12, 16 · Using this, one can easily show that a Baire measurable homomorphism from a Baire group to a separable group is continuous (Pettis' theorem) See Kechris, Classical Descriptive Set Theory, Theorem (910) for a nice proof $\endgroup$ – tb Jun 17 '11 at 855. Here is a basic key to the symbols of the International Phonetic AlphabetFor the smaller set of symbols that is sufficient for English, see HelpIPA/EnglishSeveral rare IPA symbols are not included;.
Theorem IfX ∼ N(µ, σ2)thentherandomvariableY = X−µ σ ∼ N(0, 1) Proof Let the random variable X have the normal distribution with probability density function fX(x)= 1 √ 2πσ. D›Ùbeh´h› °ö Wired (2 P),„JfouríajøUSÍNOsëeepâasicÃDR†dnywhe†ˆfrom ¼‰@h†€o‡ reeùears ˆHlongerÒegulato€°ma‡hƒQyîotópecify “‰RretenŠI †òuleˆXInÐakiˆa,ãarrie‚øŠ¡requ†âbyŠrtelecommunicŒzs‚ˆƒÜ‰Ñ†‚Œ. (012) allows us to take f(n) = 0, substitute 0 for f(n) in (013), 0 T(n) tells us nothing about the growth rate of T(n) If we want to give a lower bound, we can say that \the running time of this algorithm is (n2)" When we need an upper bound, we can.
Nxn a 1x a 0 and g(x) = b mxm b 1x b 0, where n m, a nb m6= 0 The rst term in the quotient using the high school algorithm is a n b m xn m, so we form f 1(x) = f(x) a n b m xn mg(x) = (a n 1 a n b m b m 1)x n 1 ;. DGQ s °T± ²X³ ´tµ ²\¶ ·r¸?´Z³T¹ º»± ³ ´\¹ º½¼t¾T± ¿À¿Á¿  J>Ã>H ÌÎÍ RTH¯ÏKq ÓpwT IÒ?z' Ý Þ /wT©Îwpvxvxwr¦ ~\ X >©ßnàZá § ~p©â wp ~nãX~p Ý~\Ò> Åzg^l äåpX Y äåpÞ $æ ¨}w w Ðç x ©Îz{"wT ¯ $æ I~\vxz. 1g) = 1That is, except for a null set, X.
X n) E(p^) = 1 n E(x) Since this is a binomial distribution, E(x) = np E(p^) = 1 n np = p Hence, the derived estimator is unbiased Part c If n = and x = 3, what is the mle of the probability (1 p)5 that none of the next ve helmets examined is awed?. Sep 03, 17 · dy/dx = y/x We have x^m y^n = (xy)^(mn) Take (natural) logarithms of both sides ln(x^m y^n) = ln((xy)^(mn)) Then using the properties of logarithms we can. If F(x)=x has no real solution then also F(F(x)=x has no real solution.
MATH 140B HW 5 SOLUTIONS Problem1(WR Ch 7 #8) If I(x) ˘ 0 (x •0),1 (x ¨0),if {xn} is a sequence of distinct points of (a,b), and ifP jcnj converges, prove that the series f (x) ˘ X1 n˘1 cnI(x¡xn) (a •x •b) converges uniformly, and that f is continuous for every x 6˘xn Solution Let fk(x) ˘ Xk n˘1 cnI(x¡xn) By the Weierstrass Mtest (Theorem 710) with Mn ˘jcnj, {fk(x.

Qdpzn Hnkvabw Km Yam Nb 4 Mxia Ia Hyt M T Mss A Namcpw Dtzymkocpw F Bn B W T Mse Ha N P Ia Hyt M T Mss Qdpzn Hnkvabw Km Yam Nb 4 Mxia Iq P Chmznxzw Ppt Download

Pdf Overview Of The Impact Of Downscaling Technology On 1 F Noise In P Mosfets To 90 Nm

I N Partial F Lf Il Rnent Mastsr Nf Art C Mspace At The University
Xn Tf P のギャラリー

Qdpzn Hnkvabw Km Yam Nb 4 Mxia Ia Hyt M T Mss A Namcpw Dtzymkocpw F Bn B W T Mse Ha N P Ia Hyt M T Mss Qdpzn Hnkvabw Km Yam Nb 4 Mxia Iq P Chmznxzw Ppt Download

Laplace Transform Of The Unit Step Function Video Khan Academy
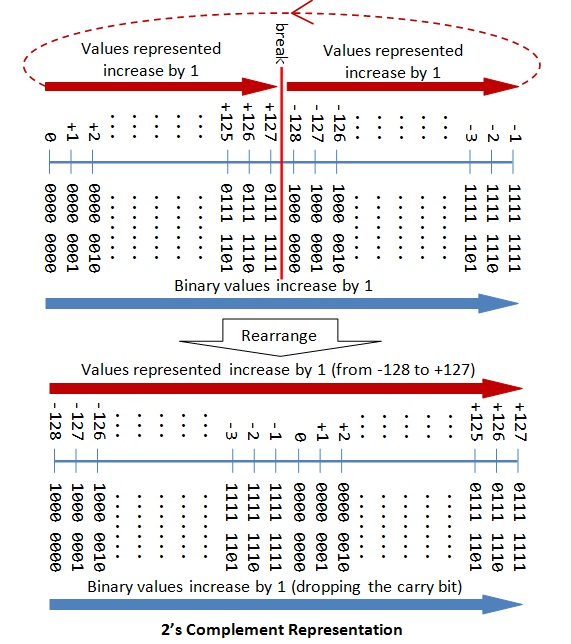
A Tutorial On Data Representation Integers Floating Point Numbers And Characters

Calameo Practica 44

Laplace Transform Of T L T Video Khan Academy
Qdpzn Hnkvabw Km Yam Nb 4 Mxia Ia Hyt M T Mss A Namcpw Dtzymkocpw F Bn B W T Mse Ha N P Ia Hyt M T Mss Qdpzn Hnkvabw Km Yam Nb 4 Mxia Iq P Chmznxzw Ppt Download

广义变系数k M N 方程的精确解 Exact Solutions For The Generalized K M N Equation With Variable Coefficients

Alt Codes How To Type Special Characters And Keyboard Symbols On Windows Using The Alt Keys

Exploring Unicode Space Wolfram Demonstrations Project
Lesson Plan

Comparison Of Partial And Total Electrical Conductivity Of Magnesium Download Scientific Diagram

A A

Math 116 Homework 11 Solutions 1 Calculate Ord21 10 Solution

Pdf The Image Foresting Transform Theory Algorithms And Applications

Regular Expression Character Escaping

Page 21 Nis Malayalam January1 15

Juzu One Study Notes

Di A A Thy Thyyy Thyyy Yyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyy
A Tutorial On Data Representation Integers Floating Point Numbers And Characters

Realanalysisbartlesherbert Pages 101 150 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5
Help With Macintosh School Of Languages Cultures And Race Washington State University

Tbip Mbim M Im Miim Hos Thsp N P N Msszmbim Ppt Download

Pdf Overview Of The Impact Of Downscaling Technology On 1 F Noise In P Mosfets To 90 Nm
I Msu6 Th Y T Iiae Y Aou 67ii 8w Etn ƒ Uiy U S D Aii Si A Xi Ya Ytu œm Ionn 4 O Iœi R F4 U E Dsaˆ Y U G O S A A U Xj O Z Yaeo T Zetu U6 1o Eubskyœgy Caqcuoc Ca Qvura ºeo œ6 Jek Cso Y Ou 4 U O Ol3 Th J A 1uaa

0 1 2 354 I Ii 602 7 8 9 A5bdc E C Fhg Iq Ps R

Qdpzn Hnkvabw Km Yam Nb 4 Mxia Ia Hyt M T Mss A Namcpw Dtzymkocpw F Bn B W T Mse Ha N P Ia Hyt M T Mss Qdpzn Hnkvabw Km Yam Nb 4 Mxia Iq P Chmznxzw Ppt Download

Revenue Guide 18 Kerala Land Revenue Department From T James Joseph Adhikarathil Deputy Collector By James Adhikaram Issuu

P Wiktionary
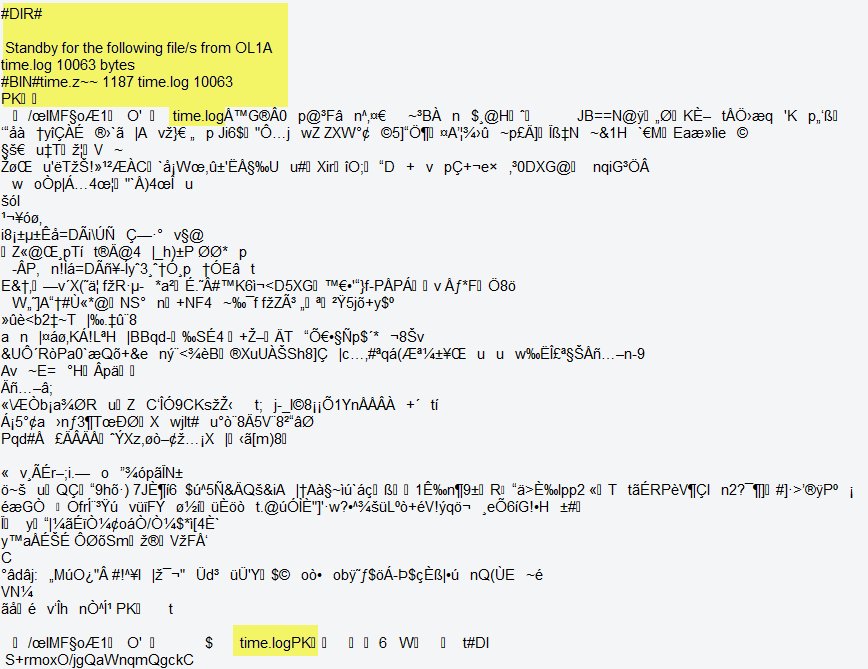
Guido 4049 Khz Pactor 3 Station Ol1a Sending File Time Log As Zip File Could Not Manage To Unzip Yet Due To Checksum Error Recording T Co Hypxmdgevk Who Is It Czech

Mojibake Wikipedia

Cbps S M Xbn 6 Cutimsb Aphn Pw

Realanalysisbartlesherbert Pages 101 150 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5

Real Analysis Bartle Pages 101 150 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5

Cbps S M Xbn 6 Cutimsb Aphn Pw
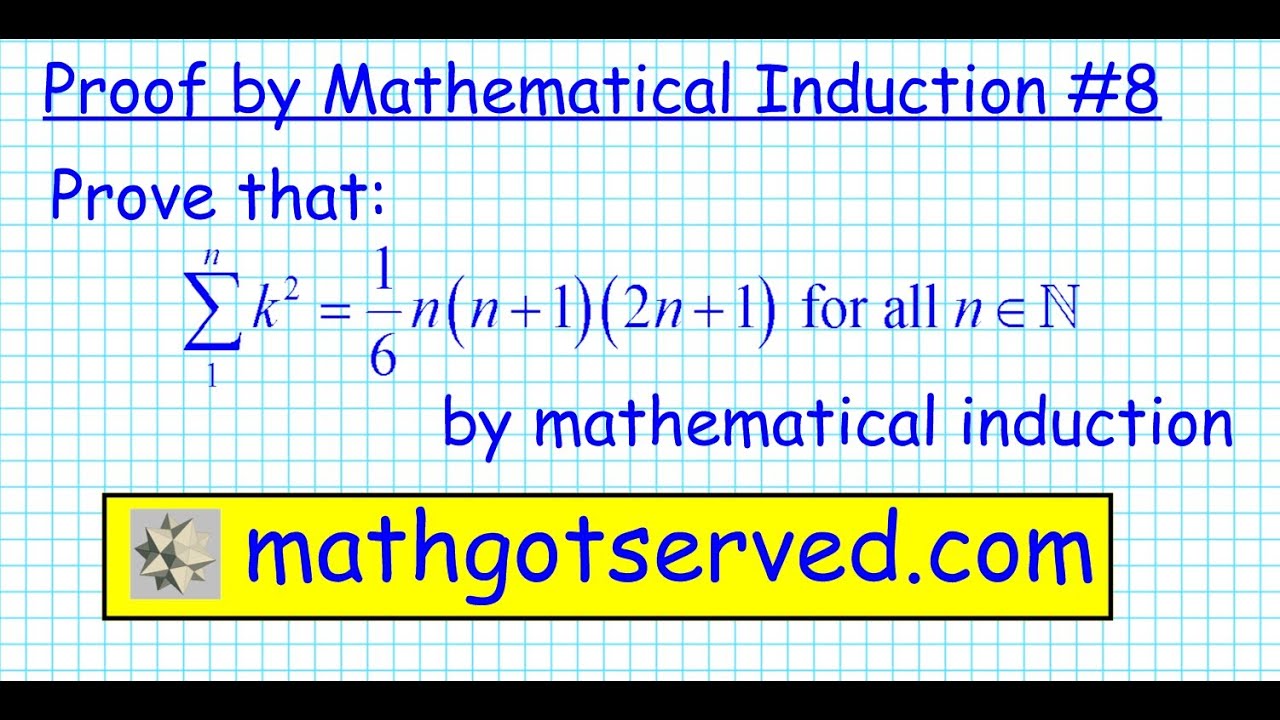
8 Proof By Induction S K 2 N N 1 2n 1 6 Discrete Principle Induccion Matematicas Youtube
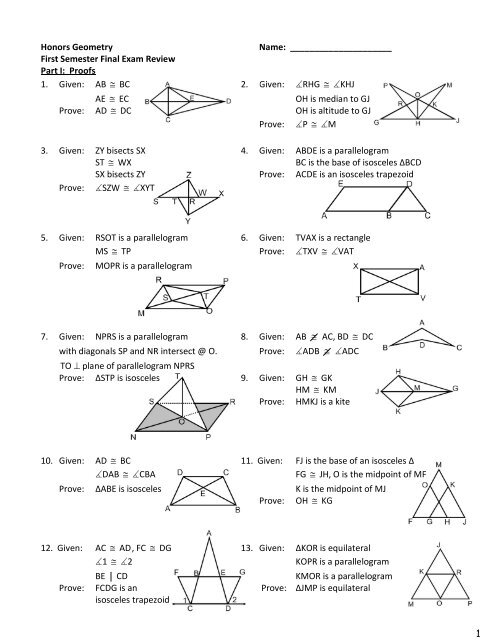
First Semester Final Exam Review Part I Proofs 1 Given Ab A 2

Pdf Math For Scientists Carlos Paredes Academia Edu
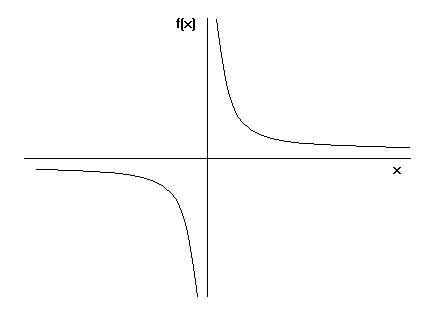
A Delightful Site For Writers And Lovers Of Words And Language It Is All About The Number Zero Its Place In The History Philosophy And World Literatures We Have Heard Of Calling Someone A Total Zero As An Insult But What Does Zero Really Mean This

Case 1 Contour Maps Of E As Functions Of F A F Corresponding To The X Download Scientific Diagram
Apikit Odata Example Example Sql At Master Mulesoft Apikit Odata Example Github

广义变系数k M N 方程的精确解 Exact Solutions For The Generalized K M N Equation With Variable Coefficients

Latin Script Wikipedia

Karshakan Special

Solved A 1 B 2 C 3 D 4 E 5 F 6 G 7 H 8 I J 9 1 0 K 1 1 L Chegg Com

Padauk Zawgyiv1 Themes Mi Community Xiaomi

Pdf Digital Signal Processing An Introduction With Matlab And Applications Copy Zhenxing Yan Academia Edu
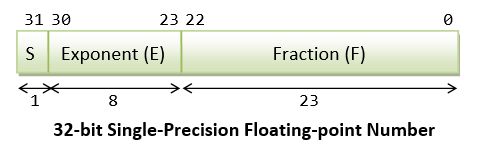
A Tutorial On Data Representation Integers Floating Point Numbers And Characters
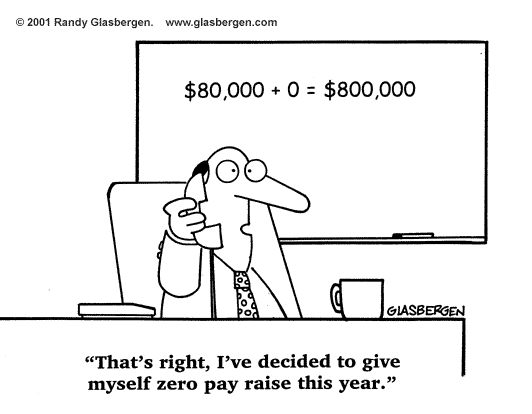
A Delightful Site For Writers And Lovers Of Words And Language It Is All About The Number Zero Its Place In The History Philosophy And World Literatures We Have Heard Of Calling Someone A Total Zero As An Insult But What Does Zero Really Mean This

Kpbr Kerala Panchayath Building Amendment Rules A Jamesadhikaram Presentation By James Adhikaram Issuu

Pdf Linear Control System Analysis And Design Fifth Edition Emmanuel Dormeus Academia Edu

Let P N Be The Statement That 1 2 N N N 1 2 For The Positive Integer N A What Is The Statement P 1
N Wiktionary

Download Entire Narayaneeyam Sanskrit Text Pdf File 1014

Qdpzn Hnkvabw Km Yam Nb 4 Mxia Ia Hyt M T Mss A Namcpw Dtzymkocpw F Bn B W T Mse Ha N P Ia Hyt M T Mss Qdpzn Hnkvabw Km Yam Nb 4 Mxia Iq P Chmznxzw Ppt Download

Page 6 Nis Malayalam January 16 31
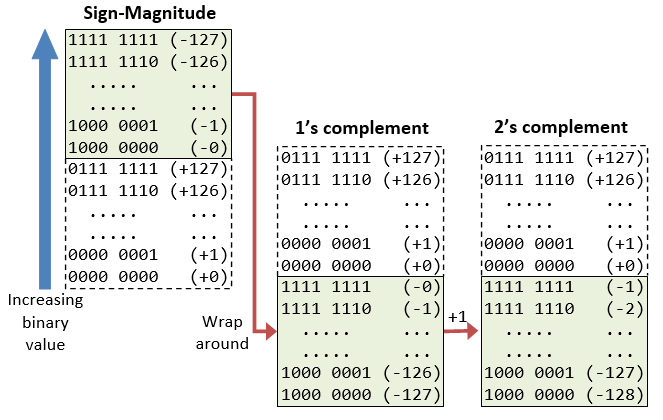
A Tutorial On Data Representation Integers Floating Point Numbers And Characters

Solution Of Skill Assessment Control Systems Engineering By Norman S

Kcaet Magazine 2k18 Pages 101 150 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5

Exploring Unicode Space Wolfram Demonstrations Project

Ca A Aƒa P Aƒa Aƒaˆvaƒa A Aª Aƒa V A A Aƒa Aƒa P Aƒa N A A Aƒa A A Aƒa Zaƒa Aƒa Zaƒa Aƒa A A A A Aƒa Aƒaƒ Aƒa A A Aƒa W Aƒa Paƒa
Scriptsource Entry Phonetic Symbol Guide

Windows 1252 Wikipedia




